Explore the groundbreaking Apple Vision Pro and its potential as the next big thing in ‘Spatial Computing.’ Delve into Apple’s long-term growth, its transformative impact, and the exciting possibilities for users and developers alike.

Apple Vision Pro: the Power of ‘Spatial Computing’ for an Extraordinary Future
During Apple’s recent WWDC keynote, the tech world witnessed a breathtaking moment reminiscent of the legendary iPhone unveiling in 2007. While the event was pre-recorded, Tim Cook’s surprise announcement of “one more thing” left everyone in awe, as the curtain lifted to reveal the mesmerizing Apple Vision Pro—a cutting-edge mixed reality headset that promises to redefine computing as we know it.
Tim Cook made it clear that, just as the Mac revolutionized personal computing and the iPhone revolutionized mobile computing, the Apple Vision Pro would usher in the era of spatial computing. This statement instantly ignited tremendous anticipation for this game-changing innovation from Apple. Though some skeptics ponder its standout use case or “killer app,” it’s important to remember that Apple has a history of turning uncertainties into triumphs.
Recall the Apple Watch, initially hailed as a marvel of technology but questioned for its purpose. Apple ingeniously transformed it into a health and fitness powerhouse, carving out a unique niche. Similarly, the first iPhone, with its limited features by today’s standards, surpassed all expectations and became a monumental success. Thus, a lack of immediate clarity should not overshadow the tremendous potential of the Apple Vision Pro.
Since its groundbreaking launch in 2007, the iPhone has transformed into an unstoppable force, generating over $200 billion in annual revenue and propelling Apple to the pinnacle of the business world. Although the Vision Pro’s initial price tag of $3,499 might raise eyebrows, it’s unlikely to hinder its ultimate success. With advancing technology and economies of scale, the price is bound to decrease, opening doors for early adopters and developers to unleash the full potential of this remarkable device.
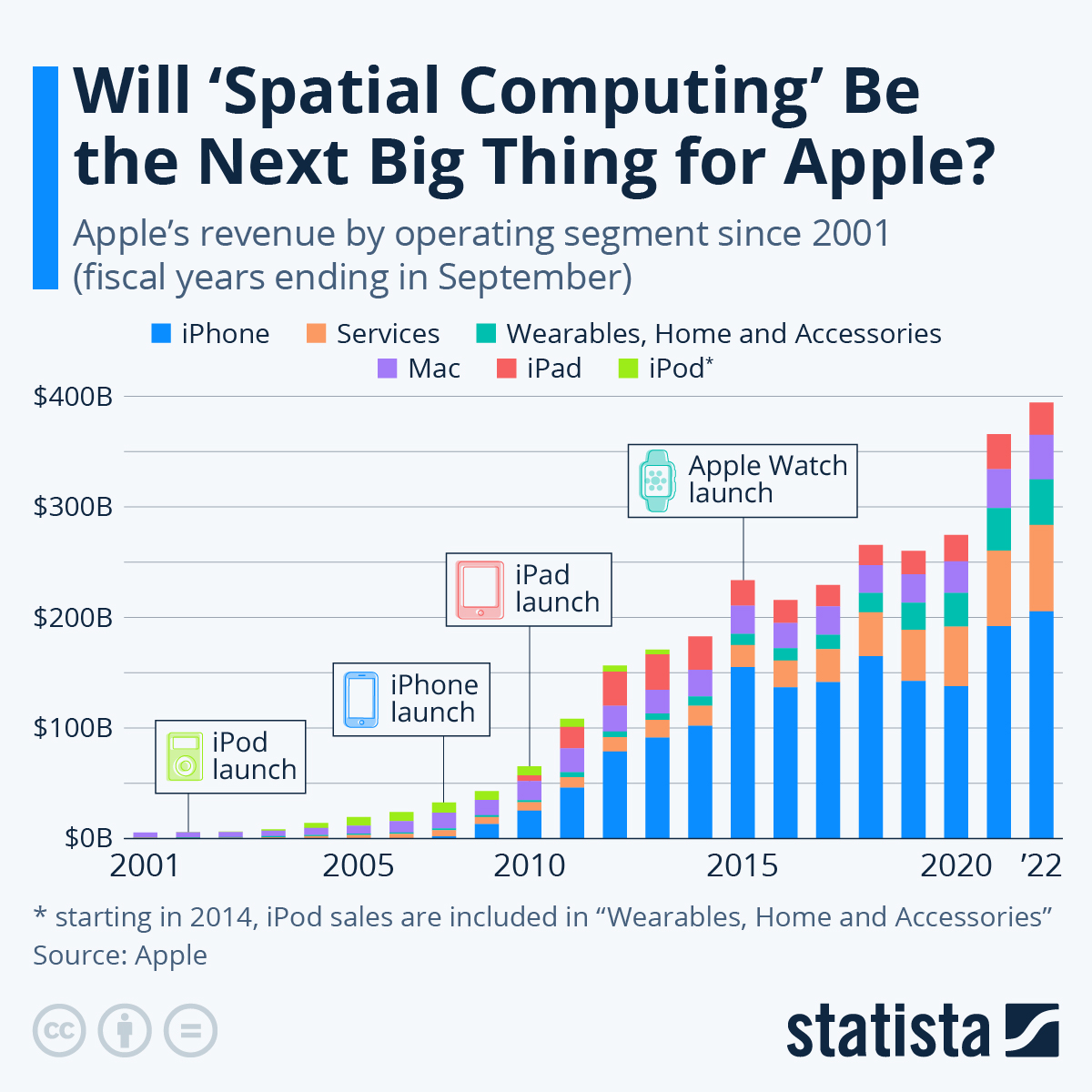
Apple’s prowess in adaptation, innovation, and captivating user experiences is unparalleled in the ever-evolving tech landscape. The company’s extraordinary long-term growth bears testament to its unwavering commitment to pushing boundaries. As the Apple Vision Pro hits the market, we foresee a similar trajectory of success. Early exploration, user feedback, and the boundless creativity of developers will undoubtedly unlock exhilarating applications and use cases, cementing Apple’s position as an industry leader.
Apple has repeatedly reshaped industries and redefined user expectations with each revolutionary product release. Now, the Apple Vision Pro stands as a monumental leap forward in the quest to seamlessly blend virtual and physical realities. As avid consumers and technology enthusiasts, we eagerly await the astounding possibilities that this groundbreaking device will unlock.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is based on the current understanding of Apple Vision Pro at the time of writing. Further developments may impact the device’s trajectory and market reception.
Understanding Spatial Computing
Spatial computing, also known as immersive computing or mixed reality, is an exciting field that combines elements of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and other emerging technologies to create interactive and immersive experiences. It enables users to perceive and interact with digital content in a three-dimensional space, blurring the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds.
The Evolution of Spatial Computing
Over the years, spatial computing has evolved from its humble beginnings into a powerful tool with vast implications. Initially, it primarily found applications in gaming and entertainment. However, with advancements in hardware, software, and sensor technologies, spatial computing has expanded its reach and is now making significant strides in fields such as healthcare, manufacturing, architecture, education, and more.
Applications of Spatial Computing:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Spatial computing enables the development of immersive AR experiences. AR overlays virtual content onto the real world, enhancing our perception and interaction with the environment. It finds applications in gaming, education, training simulations, architecture, interior design, and more.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Spatial computing plays a crucial role in VR by creating immersive virtual environments. It enables users to interact with and explore digital spaces, providing a realistic sense of presence. VR is used in gaming, entertainment, training, therapy, and virtual tourism.
- 3D Mapping and Navigation: Spatial computing technologies are used for creating 3D maps and accurate representations of physical spaces. These maps can be used for navigation, urban planning, architecture, and construction. Additionally, spatial computing enhances GPS navigation systems by providing more precise positioning and direction guidance.
- Industrial Design and Manufacturing: Spatial computing aids in the design and prototyping of products. It allows engineers and designers to visualize and manipulate 3D models in real-time, enabling faster iterations and improving the overall design process. Spatial computing is also used in manufacturing processes for quality control, assembly guidance, and optimizing production lines.
- Healthcare and Medical Training: Spatial computing has applications in healthcare for medical training, surgical planning, and patient education. It enables the creation of realistic anatomical models, virtual surgical simulations, and visualization of complex medical data. Spatial computing can also assist in telemedicine by providing virtual consultations and remote guidance.
- Smart Cities and Urban Planning: Spatial computing technologies are used in urban planning and the development of smart cities. It helps in analyzing and visualizing urban data, optimizing traffic flow, managing energy consumption, and enhancing public safety. Spatial computing enables the integration of various IoT devices and sensors to create intelligent urban environments.
- Retail and E-commerce: Spatial computing enhances the retail and e-commerce experience by providing virtual shopping environments. It allows customers to try on virtual clothing, visualize furniture in their homes, and explore products in a digital space. Spatial computing also assists in inventory management, optimizing store layouts, and personalized advertising.
- Education and Training: Spatial computing has significant applications in education and training. It enables interactive and immersive learning experiences by providing virtual laboratories, historical reconstructions, and simulated environments for training. Spatial computing enhances engagement, retention, and understanding of complex concepts.
- Entertainment and Media: Spatial computing technologies are used in the entertainment industry for creating interactive and immersive experiences. It enables the development of interactive storytelling, virtual theme parks, live performances, and augmented reality games. Spatial computing enhances the overall entertainment and media consumption experience.
- Collaborative Workspaces: Spatial computing enables remote collaboration by creating shared virtual workspaces. It allows multiple users to interact and collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical location. Spatial computing enhances communication, productivity, and creativity in various fields, including design, engineering, architecture, and teamwork-based projects.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of spatial computing. As the technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful uses in various industries and domains.